Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Engineering and Technical Center of Light Manipulations & Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optics and Photonic Device, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
2 XXL—The Extreme Optoelectromechanics Laboratory, School of Physics and Electronics Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
3 Joint Research Center of Light Manipulation Science and Photonic Integrated Chip of East China Normal University and Shandong Normal University, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200241, China
4 Collaborative Innovation Center of Light Manipulation and Applications, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250358, China
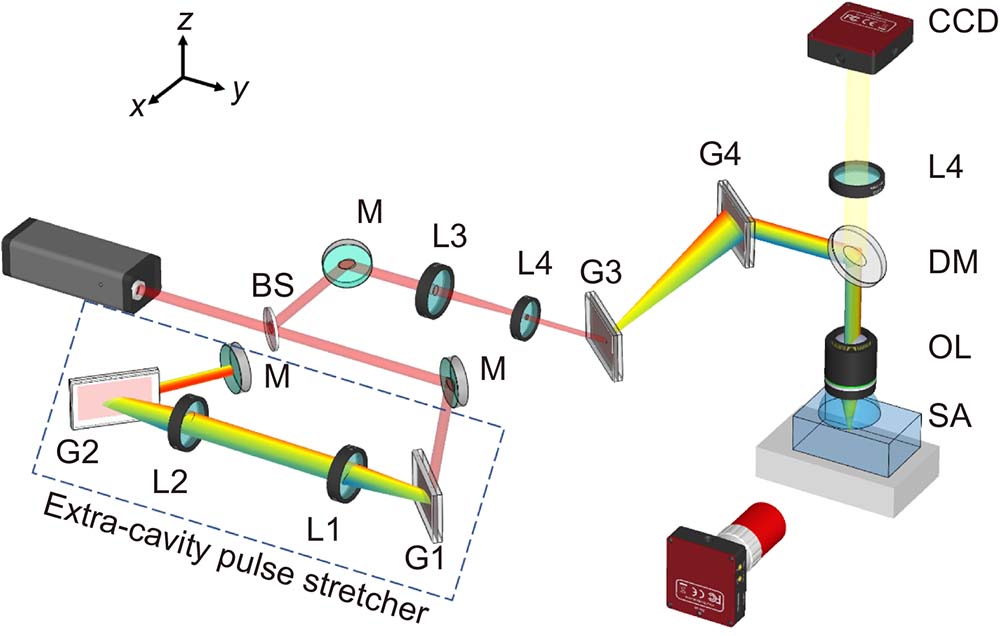
To improve the processing efficiency and extend the tuning range of 3D isotropic fabrication, we apply the simultaneous spatiotemporal focusing (SSTF) technique to a high-repetition-rate femtosecond (fs) fiber laser system. In the SSTF scheme, we propose a pulse compensation scheme for the fiber laser with a narrow spectral bandwidth by building an extra-cavity pulse stretcher. We further demonstrate truly 3D isotropic microfabrication in photosensitive glass with a tunable resolution ranging from 8 μm to 22 μm using the SSTF of fs laser pulses. Moreover, we systematically investigate the influences of pulse energy, writing speed, processing depth, and spherical aberration on the fabrication resolution. As a proof-of-concept demonstration, the SSTF scheme was further employed for the fs laser-assisted etching of complicated glass microfluidic structures with 3D uniform sizes. The developed technique can be extended to many applications such as advanced photonics, 3D biomimetic printing, micro-electromechanical systems, and lab-on-a-chips.
simultaneous spatiotemporal focusing technique pulse compensation pulse stretcher 3D isotropic fabrication chemical etching Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(10): 230066
华东师范大学精密光谱科学与技术国家重点实验室, 上海 200241
提出了一种在玻璃表面制备嵌入式亚微米金属线的方法。首先利用飞秒激光直写技术在玻璃表面烧蚀出亚微米线宽的凹槽,然后采用连续流化学镀工艺在样品表面沉积金属薄膜,再经过热处理和机械抛光,可实现玻璃表面嵌入式亚微米线宽金属结构的可控制备。将飞秒激光烧蚀的阈值效应与连续流化学镀相结合,可制备出最小线宽约为0.66 μm的金属银线。四探针法测试结果表明,制备的亚微米金属银线具有良好的导电性,其电阻率约为体积银电阻率的1.2倍。
激光技术 飞秒激光烧蚀 石英玻璃 阈值效应 连续流化学镀 亚微米金属线





